Reduction of direct impact on the environment

Environment protection
We see environment protection as an integral part of our production activities and consider the increase of environmental safety level one of our top-priority tasks. Our company actively interacts with federal and regional government bodies in order to determine the Company’s zone of responsibility and develop alternative solutions for reduction of the negative impact on the environment.
Documentary support of ecological safety and environment protection
In order to establish uniform requirements for all branches of IDGC of the North-West in the field of environment protection the Company approved the Environmental Policy. The Environmental Policy of IDGC of the North-West was developed in accordance with the state strategy in the field of ecological safety and rational use of natural resources and requirements of environmental legislation of the Russian Federation.
Top-priority environmental goals
We see environment protection as an integral part of our production activities and consider the increase of environmental safety level one of our top-priority tasks. Our company actively interacts with federal and regional government bodies in order to determine the Company’s zone of responsibility and develop alternative solutions for reduction of the negative impact on the environment.
Top-priority environmental goals
According to the approved Program for Implementation of the Environmental Policy the top-priority goals of JSC IDGC of the North-West in the field of environment protection are:
- reduction of negative environmental impact; and
- evaluation of environmental activity for the purpose of its improvement.
Realization of the Program for Implementation of the Environmental Policy allowed reducing a negative impact on the environment and increasing the Company’s social responsibility in
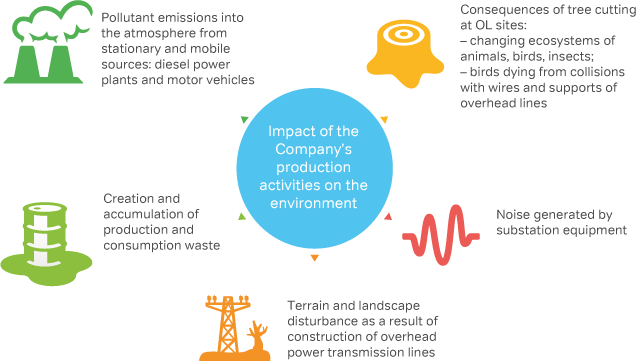
The primary objectives of JSC IDGC of the North-West in the field of environment protection are:
- minimization of environment pollution by the processed oil products through proper repair of oil-receiving devices, replacement of oil-filled equipment by SF6 or vacuum counterparts;
- development and approval of projects for sanitary protection zones of artesian wells used for water supply to the branches’ facilities;
- improvement of the Program for Implementation of the Environmental Policy of the Company, assessment of risks and impact of production activities on the environment.
The Company’s strategic environmental targets for the period until 2014 are:
- development of measures for improvement of the management system in the field of environment protection and nature management;
- environmental audit for integrated assessment of environmental activities.
Qualification of the Company’s environmental personnel
The Company’s management and employees were trained in
Level of impact on the environment
Due to the constant increase in the volumes of repair works and, hence, waste the major part of payments for negative impact on the environment is presented by payments for waste disposal. Payments for emissions from stationary and mobile sources and for discharge of sewage waters are minimum, which evidences a minor level of impact of the Company’s production activities on the environment. As a result of continuous activities aimed at reduction of negative impact on the environment, payments for negative impact on the environment decreased by 62% compared to 2011 and in 2012 were RUB 6.791 million.
Dynamics of payments for the negative impact on the environment in 2011-2012, RUB thousand
| Description | 2012 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|
| Total, including: | 6,791.751 | 10,981.50 |
| permissible volumes | 4,615.754 | 2,724.02 |
| above-limit volumes | 2,175.997 | 8,257.53 |
| Discharge to water reservoirs, including: | 130.674 | 124.100 |
| permissible volumes | 130.174 | 123.247 |
| above-limit volumes | 0.500 | 0.854 |
| Emissions to the atmosphere, including: | 548.386 | 263.875 |
| permissible volumes | 232.839 | 141.748 |
| above-limit volumes | 315.547 | 122.127 |
| Waste disposal, including: | 6,112.691 | 10,593.56 |
| permissible volumes | 4,252.741 | 2,459.02 |
| above-limit volumes | 1,859.950 | 8,134.54 |
Decrease in above-limit payments for the negative impact on the environment compared to 2011 was due to the following reasons:
- permits (waste disposal limits) were developed and approved in the production departments of branches of IDGC of the North-West;
- draft normative standards for waste formation and limits on waste disposals were adjusted taking into account the 2011 data on exceeding the established waste disposal limits.
Nature protection measures
Modern equipment installed in the process of modernization of networks and decommissioning of obsolete equipment enable us to reduce the negative impact on the environment in electric power transportation and distribution.
Branches of IDGC of the North-West carry out works for continuous improvement of territories of the bases of electric grids.
Production environmental control and internal audit
Environmental safety in the Company’s branches and in its area of influence is ensured by carrying out production environmental control (PEC) — internal self-control carried out by specialists responsible for this area of activities. The key objectives of PEC are prevention and prompt elimination of consequences of damage caused to the environment by the Company’s activities.
The procedure for production environmental control in branches of IDGC of the North-West is determined by schedule plans made in each production department separately for each type of influence and controlled environment (emissions, air, waste, etc.) and updated annually.
Within the framework of production environmental control in
Based on the results of the audit conducted non-conformities to legal requirements of the RF were detected. On the basis of audit reports and notes, plans of actions were developed and at the moment active measures to remedy these non-conformities are taken.
Laboratory analytic control is carried out by external certified laboratories (by regions) on a contractual basis in all production departments of the branches. The content of pollutant substances in emissions, underground and sewage waters is controlled under agreements with certified laboratories.
The terms and conditions of the subsoil license agreement are fulfilled in full, laboratory analysis of water from wells by quality indicators and composition is carried out (odor, color, рН, chemical elements, etc.).
| Controlled object | Frequency of controls | Controlled parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Emissions of diesel power plants (DPP) | Once a quarter | nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon black, benzopyrene |
| Emissions of boiler houses | Once a year | nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, benzopyrene |
| Subsoil water | Once a year | conformity of water quality to state sanitary and epidemiological standards and rules |
| Sewage water from REG bases | Twice a year | pH, suspended solids, BOD, petroleum products |
| Sewage water from DPP bases | Once a quarter | pH, suspended solids, BOD, ammonium ions, phosphate ions, anionic surfactants, petroleum products |
Waste management
The main focus in environment protection measures was on arrangement of places of temporary accumulation, collection and transfer to specialized companies for processing, use and placement of waste of hazard class
Materials from recycled or reused waste are not applied.
The main amount of the formed waste is of the hazard classes 4 and 5.
In order to reduce the environmental impact a part of waste with the hazard class
We implement a program for gradual decommissioning of equipment containing polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB). The Company developed a schedule for decommissioning of such equipment until 2020.
In 2011 51 PCB containing condensers were transferred for utilization with expenses amounting to RUB290.0 thousand, inclusive of VAT. The receiving organization carried out removal of the equipment with further transfer for utilization.
In 2012 34 PCB containing condensers were transferred for utilization with expenses amounting to RUB240.12 thousand, inclusive of VAT.
In 2013 the branches of IDGC of the North-West plan to transfer for utilization PCB containing condensers for the total amount of RUB465.40 thousand, inclusive of VAT (10.06 tons in physical terms).
Diesel power plants are the largest contributors to air pollutant emissions.
The major part of consumed water (60%) is used for household and drinking needs and the remaining 40% are used for industrial needs.
Dynamics of class 1-4 waste formation amounts for 2010-2012
| Waste hazard class | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 6.89 | 8.15 | 5.77 |
| Class 2 | 19.57 | 17.79 | 7.85 |
| Class 3 | 624.30 | 163.41 | 217.69 |
| Class 4 | 7,386.39 | 6,363.14 | 6,118.43 |
| Class 5 | 3,117.90 | 2,789.16 | 6,743.90 |
| Total | 11,155.07 | 9,341.67 | 13,093.70 |
Protection devices for birds
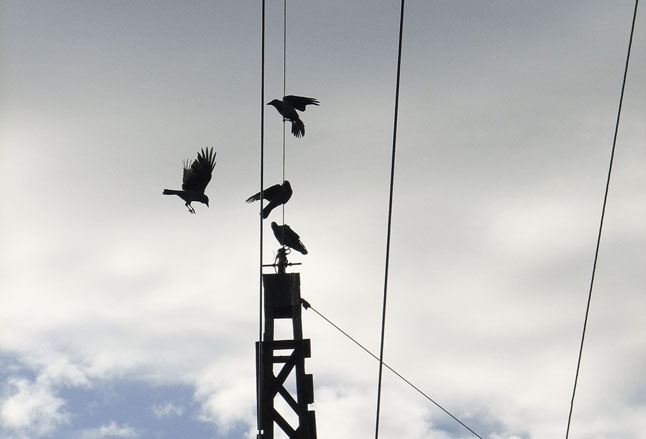

Major impacts on biodiversity in any territories include clearing of OL sites in bird nesting areas, direct hunt by man, disturbance factors.
The process of design and construction of new OL include measures for preventing and reducing the risk of birds dying from contact with hot wires at sites of their attachment to support structures and from collisions with wires in flight.
Transformer substations on power lines, their nodes and working mechanisms are provided with special protective devices (fencing, covers) preventing animals from entering the substation environment and getting electrocuted.
Lines, supports and insulators are equipped with specialized bird-protective devices, including those preventing birds from nesting in areas where any contact with hot wires may occur. The Company’s branches regularly take the following technical measures for protection of wildlife, including birds:
- installation of 696 anti-bird “screens” (in
2011-2012); - installation of 263 anti-bird “hedgehogs” (in
2011-2012).







